[ad_1]

Discover
The concept that life's deepest, oldest roots have been laid down by RNA molecules that developed ever extra complexity has dominated the origins-of-life area for the previous few many years, reigning over competing theories that began as a substitute with peptides or DNA.
However lately, the sphere has shifted towards theories that embody multiple protagonist. One which's gained explicit momentum is the concept RNAs and peptides coevolved complexity, and that their intermingling sparked life as we all know it.
Now, a examine printed in Nature breathes hearth into an “RNA-peptide world” by suggesting a believable pathway for the way early RNA molecules could have enabled peptides to develop immediately on them, like mushrooms rising on a tree. These peptides could in flip have stabilized the RNA molecules, permitting them area to complexify. This coevolution of two of life's key gamers as a single combined, “chimeric” molecule could have been the very starting of protein manufacturing, and a step towards a primitive model of a ribosome.
“It seems that they may have really helped each other,” stated Claudia Bonfioa junior group chief on the Institute of Supramolecular Science and Engineering in Strasbourg, France, who wrote a commentary that accompanies the paper. Research have proven that the uncooked supplies for each peptides and RNA would possible have been current at first of life, so this paper takes the view, “Why ought to we simply deal with RNA?” Bonfio stated.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
The work opens new instructions to discover the origins of life, stated Yitzhak Tora professor of chemistry and biochemistry on the College of California San Diego, who was not a part of the analysis however is a longtime collaborator with the authors. “Now you could contemplate the interplay between two totally different biomolecules.”
It's a “extremely intriguing demonstration,” stated Andro Riosa analysis scientist on the Blue Marble House Institute of Science and NASA's Ames Analysis Heart.
The findings additionally clarify a significant chicken-and-egg conundrum that has bedeviled researchers learning life's origin: How did proteins type earlier than the evolution of the ribosome—the mobile machine that churns out proteins in fashionable cells—when the ribosome is partly made up of proteins themselves?
Dwelling Fossils
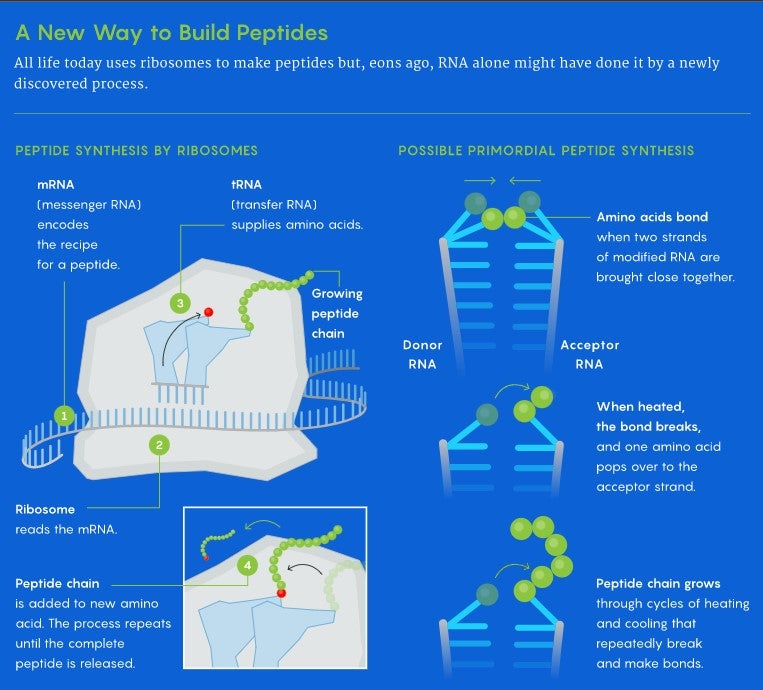
When cells must make proteins, their genes spin out lengthy threads of messenger RNA (mRNA) that encodes very exact recipes for making them. Ribosomes slide over these recipes to learn them and assemble the amino acids that correspond to every step, with the assistance of their amino acid suppliers: molecules known as switch RNA (tRNA) that constantly dive in as the method unfolds. The ribosome transfers a rising peptide chain onto every new amino acid introduced in by tRNAs. These chains get longer and longer and finally fold into useful proteins.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
It's unlikely, nevertheless, that proteins fashioned in an analogous manner 3.5 billion years in the past. The bonds that maintain the peptides on the tRNA molecules are moderately weak. And not using a ribosome out there to supply shelter, water molecules would break these bonds earlier than peptides might type, making the method unfeasible within the harsh watery circumstances of the primordial world.
However most individuals are specializing in re-creating the acquainted technique of protein translation in an easier type, stated Thomas Carellsenior writer of the brand new paper and the chair for natural chemistry on the Ludwig Maximilian College of Munich. What if historic translation appeared very totally different from its fashionable type?
Carell and his workforce began to dig into this concept, in search of stronger bonds which may have survived in primordial circumstances. That's how they zoned in on the often-overlooked molecules known as noncanonical nucleotides. The genetic code of RNA is often written with simply 4 bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil), however nucleotides with different bases are additionally current in lots of RNA molecules that do different jobs—together with serving to with protein manufacturing within the ribosome. These uncommon nucleotides can connect to amino acids with a chemical bond that's a lot stronger than the one which attaches amino acids to the tRNA molecules.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
Print a 2018 examineCarell and his workforce reported that the traditional nucleotides and the noncanonical nucleotides possible all developed on the identical time earlier than the daybreak of life. A few of these in switch and ribosomal RNAs have been current within the final common frequent ancestor of all organisms.
Right here have been “relics of an previous RNA world sitting subsequent to one another immediately on the oldest a part of the system,” Carell stated. “So we stated, OK, these are our fossils—and let's see what the fossils can inform us.”
They developed a mannequin for a distinct type of peptide-growing course of. They imagined two RNA strands capped by these uncommon nucleotides, one which they loaded with an amino acid utilizing the stronger bond. After getting the primary amino acid to hop to the second strand, they’ll reload the primary strand with one other amino acid. By cyclically heating and cooling the system, they’ll repeatedly break and make bonds between the amino acids on the 2 chains, flipping the amino acids from one strand to the opposite and lengthening the chain.
In impact, if constructing a peptide is like assembling a tower from constructing blocks, the brand new course of provides amino acids by including blocks to the highest of a rising stack, whereas ribosomal protein synthesis extends the tower by shifting it atop new items on the backside.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
Rising Peptides
Testing their concept concerned a set of experiments that Carell known as a “tedious” and “brutal tour de power”—however ultimately, they confirmed that the method might certainly produce peptides as much as 13 amino acids lengthy.
The method falls far wanting the protein translation seen in cells. A very powerful lacking function is that ribosomes are translating directions for a particular protein encoded within the mRNA. Within the novel system, “we develop comparatively random peptides,” Carell stated.
However the researchers did reach exhibiting that peptides might be constructed up purely by RNA in a stepwise method, which is “one thing that had not been carried out earlier than,” Bonfio stated. All in all, the demonstration course of is a crucial step towards molecular recognition, she stated, regardless that it's not a primitive model of a ribosome.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
“So we stated, OK, these are our fossils—and let's see what the fossils can inform us.”
“It's a extremely lovely instance of chemistry,” stated Sara Walkeran affiliate professor at Arizona State College who was not a part of the examine. However she and Lee Croninchair of chemistry on the College of Glasgow, each thought that the system is perhaps over-engineered or too unrealistic to imitate what might have occurred at first of life.
For others, nevertheless, the work's mimicry of the primordial world is much less necessary than the doorways it opens to additional examine. As a result of the findings present {that a} peptide and an RNA can evolve collectively, it's clear that “this could experimentally and chemically be carried out,” stated Nizar Saada analysis assistant professor at Nationwide Youngsters's Hospital's Heart for Gene Remedy in Ohio. An RNA-peptide world “is what the scientific neighborhood goes in the direction of now,” Saad stated.
An RNA-Peptide World
“I don't need to exchange the RNA world concept,” Carell stated. However “I believe we want an extension” to make it extra believable. He thinks that moderately than evolving their complexity individually, RNA and peptides did it collectively as a single molecule, complementing one another's capabilities.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
A coevolving chimera of RNA and peptides would supply one of the best situation for the evolution of life, Carell stated. He and his workforce discovered not solely that the RNA molecules have been serving to the peptides develop, however that the peptides have been bringing stability to the RNA molecules.
Because the construction of the chimera finally will get longer and extra complicated, the peptide portion may need stabilized the RNA sufficient for it to start out self-replicating and evolving. In the meantime, the RNA may need let the peptide half purchase a complicated sufficient construction to permit it to start out catalyzing chemical reactions. Finally, the components might have cut up aside and begin to work together in ways in which extra carefully resemble what occurs in a ribosome.
Carell and his workforce are subsequent hoping to study if they’ll get their unorthodox RNA molecules to develop particular peptides from encoded info. They then hope to see whether or not the peptide can develop catalytic capabilities which may assist the RNA to copy.
No matter successes or failures lie forward, it should all the time be onerous to know precisely what occurred billions of years in the past. “We can’t return in time, so no matter you assemble within the area, anyone can all the time say, I believe all of it occurred in a different way,” Carell stated. “And if anyone comes up with a greater mannequin, (it's) greater than welcome. That is how science develops.”
ADVERTISEMENT
Nautilus Members take pleasure in an ad-free expertise. Log in or Be a part of now .
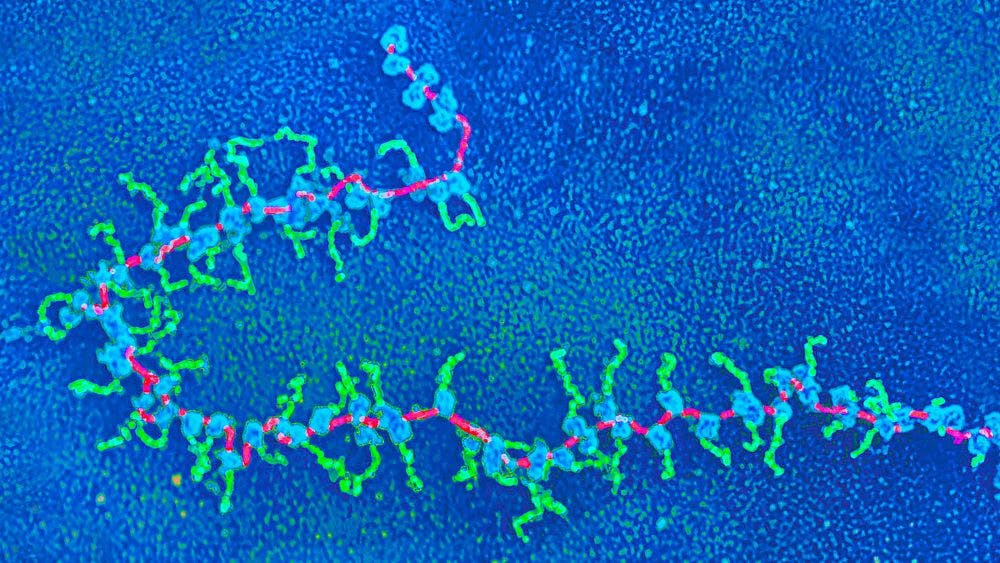
Lead picture: Buildings in residing cells known as polyribosomes present protein synthesis in motion, as seen on this micrograph. Ribosomes (blue) transfer alongside a strand of messenger RNA (magenta), studying its encoded contents and assembling strands of peptides (inexperienced). Credit score: Elena Kiseleva/Science Supply
This text was initially printed on the Quanta Abstractions weblog.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink